What is gypsum ?
Release Time:2022-09-29
Table of Contents
Overview of gypsum powder
Gypsum is a monoclinic crystal system mineral, and its main chemical component is calcium sulfate (CaSO4) hydrate. Gypsum is a widely used industrial and construction material. Can be used for cement retarder, gypsum building products, model making, medical food additives, sulfuric acid production, paper filler, paint filler, etc.
The microporous structure of gypsum and its products and heating dehydration, so that they have excellent sound insulation, heat insulation and fire performance.
Classification of gypsum
Gypsum is commonly referred to as gypsum and anhydrite two minerals.
The gypsum is calcium sulfate dihydrate (Ca [SO4] ·2H2O), also known as dihydrate gypsum, hydrogypsum or anhydrite. The theoretical components are CaO32.6%, SO346.5%, H2O+20.9%, monoclinic crystal system. The crystal is plate shape, usually dense block or fiber shape, white or gray, red, brown, glass or silk luster. Mohs hardness is 2, cleavage parallel {010} complete, density 2.3g/cm3;
The anhydrite is anhydrous calcium sulfate (Ca [SO4]). Its theoretical components are CaO41.2% and SO358.8%. The crystals are plate-like, usually dense bulk or granular, white or off-white, glassy luster, Mohrinis hardness is 3 ~ 3.5, cleavage parallel {010} complete, density is 2.8 ~ 3.0g/cm3. The two kinds of gypsum are often produced together and can be transformed into each other under certain geological processes.
Physicochemical properties of gypsum
Natural dihydrate gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) is also known as raw gypsum. After calcination and grinding, β-type hemihydrate gypsum (2CaSO4·H2O) can be obtained, namely, building gypsum, also known as plaster of Paris and stucco. If the calcination temperature is 190 °C, the model gypsum can be obtained, and its fineness and whiteness are higher than those of the building gypsum. If will raw gesso be in 400-500 °C or above 800 °C below calcination, get floor gesso immediately, its condense, harden slower, but the strength after harden, wear resistance and water resistance are better than common building gesso.

Color: Usually white, colorless, colorless transparent crystal called through gypsum, sometimes because of impurities into gray, light yellow, light brown and other colors. The white stripes. Transparent. Glass luster, cleavage surface pearl luster, fiber polymerization filament luster.
Hardness: 1.5~2. (It changes slightly in different directions).
Relative density: 2.3.
Under polarizing lens: Colorless. Biaxial crystal (+). 2 v = 58. Ng=1.530, Nm=1.523, Np=1.521. 2V decreases with increasing temperature and reaches zero at about 90 ° C.
During heating, there are three stages of discharging water of crystal:
1.105~180℃, one water molecule is discharged first, and then half of the water molecule is discharged immediately, which is transformed into burnt gypsum, also known as plaster of Paris or hemihydrate gypsum.
2. At 200~220℃, the remaining half of the water molecules were discharged and converted into type ⅲ anhydrite.
3. About 350℃, transformed into type ⅱ gypsum Ca[SO4]. At 1120℃, it was further transformed into anhydrite type I. Melting temperature 1450℃.
The microporous structure of gypsum and its products and the heating of water, so that they have excellent sound insulation, heat insulation and fire performance.
The application of gypsum
1. Building Materials.
(1) Gypsum board is primarily used as a finish for walls and ceilings, and is known in construction as plasterboard, “sheetrock”, or drywall. Gypsum provides a degree of fire-resistance to these materials and glass fibers are added to their composition to accentuate this effect. Gypsum has little heat conductivity, giving its plaster some insulative properties.
(2) Gypsum blocks are used like concrete blocks in building construction.
(3) Gypsum powder is also added to cement and paints used in building construction and finishing. In cement and concrete mixes, gypsum helps to increase the time it takes for concrete and cement to dry and harden, resulting in a more stable structure. In paint, gypsum powder uses a filler to adhere to the pigments and improve the paint’s texture.
2. Modeling, sculpture and art.
Plaster for casting moulds and modeling.
As alabaster, a material for sculpture, it was used especially in the ancient world before steel was developed, when its relative softness made it much easier to carve. During the Middle Ages and Renaissance, it was preferred even to marble.
In the medieval period, scribes and illuminators used it as an ingredient in gesso, which was applied to illuminated letters and gilded with gold in illuminated manuscripts.
3. Soil Conditioning and Fertilizing.
Gypsum powder is used in agriculture as a soil conditioner and fertilizer. Applying it to soil as a fertilizer contributes calcium and sulfur, two nutrients used by plants. Gypsum powder is especially beneficial to corn and soybeans, which need a lot of sulfate in the soil to thrive. The affinity gypsum mineral has for water molecules increases soil’s ability to hold water when the gypsum is worked into the soil because the positively charged calcium ions (Ca2+) in gypsum displace the positively charged sodium ions (Na+) present in the soil.
4. FDA-Approved Food Additive.
Because gypsum is considered generally safe for humans, it can be used in small amounts in food and beverage production. In the food industry, gypsum may be used as an anti-caking agent, drying agent, dough-strengthener, firming agent, color enhancer, stabilizer and thickener. Food products that may be made with gypsum include baked goods, frosting, candies, ice cream and other frozen dairy products, puddings, gelatins and pasta. Gypsum powder is also a non-active ingredient in toothpaste.
5. Medicine and cosmetics.
(1) Plaster for surgical splints.
(2) Impression plasters in dentistry.
6. Other.
(1) An alternative to iron oxide in some thermite mixes.
(2) Tests have shown that gypsum can be used to remove pollutants such as lead or arsenic from contaminated waters.
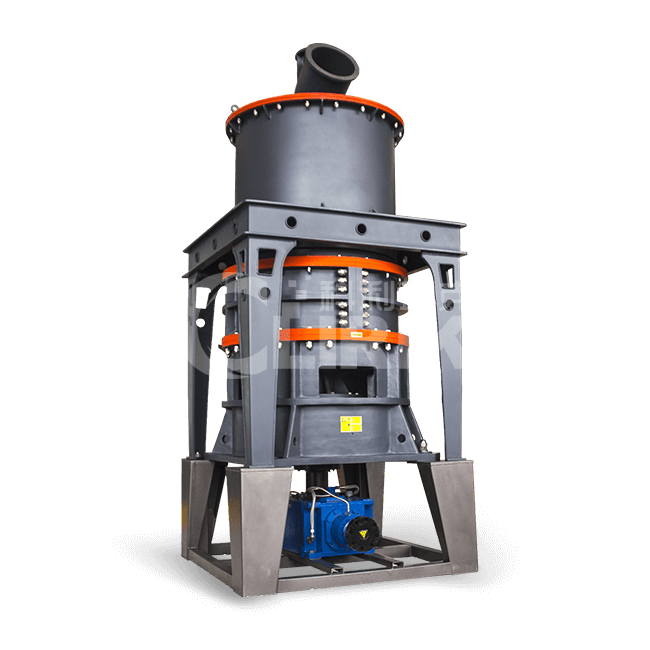
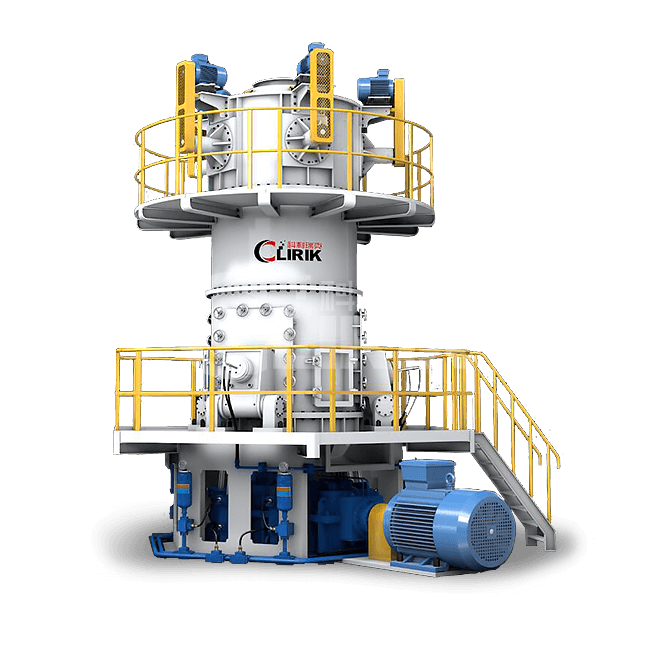
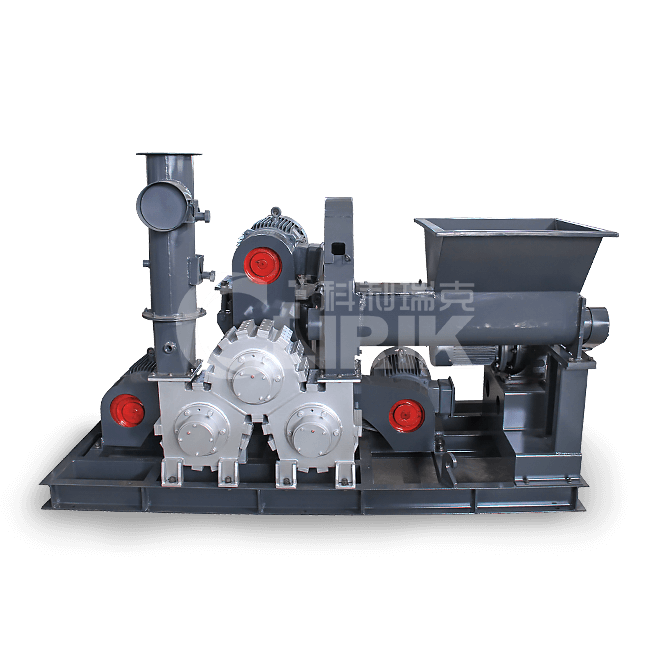
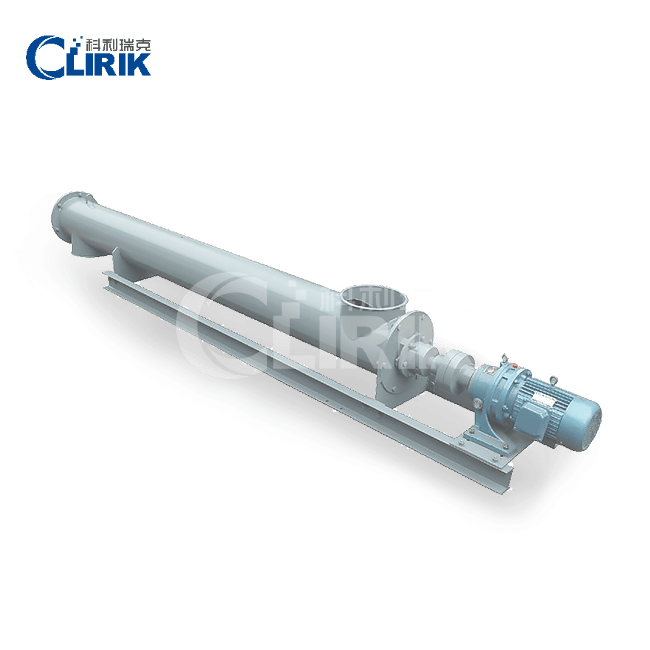
Machines for grinding gypsum powder are recommended
If you want to know more about gypsum powder and gypsum powder grinder, you can click here to consult us.
Gypsum powder crusher
Gypsum powder ultrafine grinding mill
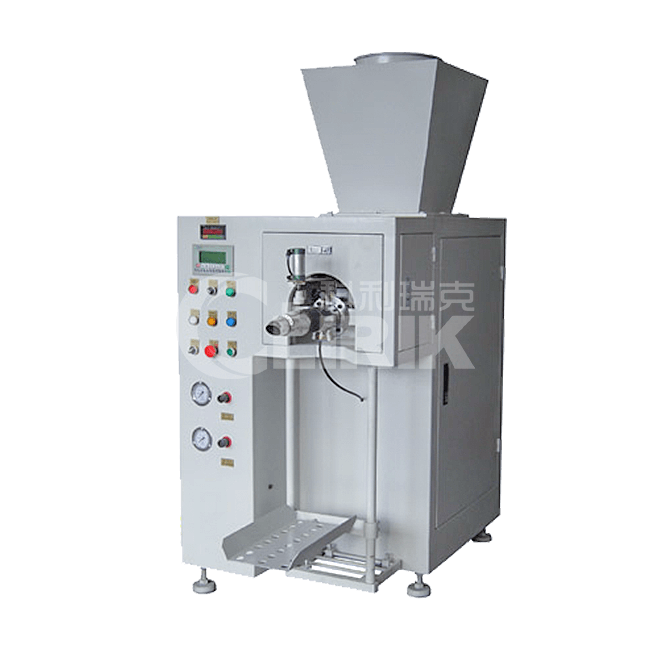
Auxiliary equipment for processing Gypsum Powder